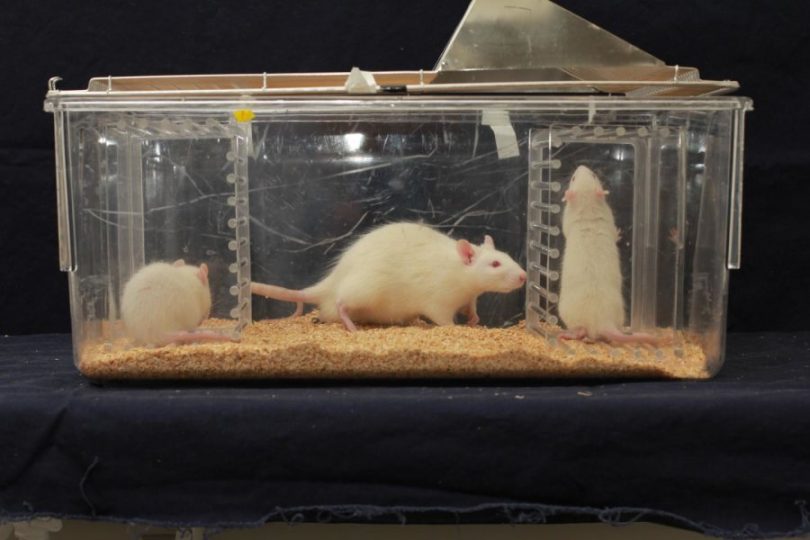
Searching for clues to complex social behaviors, experiments found that laboratory rats – much like humans – will approach distressed juveniles but avoid distressed adults — responses known as social affective behaviors, researchers report. Additionally, the brain's insular cortex region is required for proper reactions to others in distress. Further, changes in insular cortex excitability, caused by the hormone oxytocin, likely account for the social affective behaviors.Original Article
You may also like
New alloys for manufacturing freeze-dryers
Navigating the Complexities of Emerging Therapy...
INTERPHEX 2025: Preventing Spills in the Manufacturing...
Agentic AI Growth Predicted, but More Than Half of...
Microsoft and SkyCell Collaborate on Pharma Supply...
Siemens Acquires Dotmatics, Extending AI Software...
About the author
David Miller
a pharmacist, a tech enthusiastic, who explored the Internet to gather all latest information pharma, biotech, healthcare and other related industries.